C183 – ISO 6578 Klosek-McKinley LNG Density
Description
This equation is used to calculate the saturated liquid density of LNG mixtures from composition. The equation is valid at temperatures between -180°C and -140°C, and only for LNG mixtures with:
- an average molecular mass of less than 20.0 kg/kmol,
- mole fractions of N2 less than 5%,
- mole fractions of total C4 less than 5%,
- mole fractions of C5+ less than 1%,
- and no more than a “trace” of O2.
References
ISO 6578:1991 (BS 7577:1992) – Calculation procedures for static measurement of refrigerated light hydrocarbon fluids
KELTON calculation reference C183
FLOCALC calculation reference F054
KIMS calculation references K187
Inputs
The required inputs for this calculation are:
- LNG mixture composition
- Temperature at which the saturated density is required
Calculations
The LNG density is calculated from the following equation:
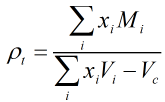
| Where | ||
| ρt | = | LNG mixture density at temperature t in °C |
| xi | = | Mole fraction of component i |
| Mi | = | Molar mass of component i |
| Vi | = | Molar volume of component i at temperature t in °C |
| Vc | = | Reduction in volume due to mixing of components at temperature t in °C |
The molar mass and volume values are obtained from the relevant tables in ISO 6578:1991.
The reduction in volume due to mixing, Vc, is calculated from:
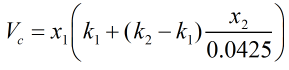
| Where | ||
| k1 | = | Correction factor due to presence of hydrocarbons |
| k2 | = | Correction factor due to presence of nitrogen |
| x1 | = | Mole fraction of methane |
| x2 | = | Mole fraction of nitrogen |
The correction factors k1 and k2 are obtained from the relevant tables in ISO 6578:1991, as a function of temperature and average molecular weight of the LNG mixture.