C127 – AGA 5 Natural Gas Energy Measurement
Description
This calculates the gross and net heating values of a natural gas for custody transfer.
References
AGA Report No.5 – Natural Gas Energy Measurement (2009)
Kelton calculation reference C127
FLOCALC calculation reference F087
KIMS calculation reference K129
Options
Heating Value Method
- Molar
- Volumetric
This option allows the user to select whether they want the known values heating values of the constituent compounds to be molar or volumetric values.
Standard Temperature
- 0°C
- 15°C
- 20°C
- 25°C
- 59°F
- 60°F
If “Molar” is selected as the Heating Value Method, this option will allow the user to select the standard temperature of the gas mixture.
Standard Conditions
- 0°C, 100kPa
- 15°C, 101.325kPa
- 20°C, 98.0665kPa
- 59°F, 14.696psi
- 60°F, 14.4psi
- 60°F, 14.65psi
- 60°F, 14.696psi
- 60°F, 14.73psi
- 60°F, 15.025psi
If “Volumetric” is selected as the Heating Value Method, this option will allow the user to select a set of standard conditions for the gas mixture.
Constants
Gas Constant – R = 8.314472 J/molK
Molar masses of supported constituents and air
| Gas | Molar Mass (g/mol) |
| Methane | 16.0425 |
| Ethane | 30.069 |
| Propane | 44.0956 |
| i-Butane | 58.1222 |
| n-Butane | 58.1222 |
| i-Pentane | 72.1488 |
| n-Pentane | 72.1488 |
| n-Hexane | 86.1754 |
| n-Heptane | 100.2019 |
| n-Octane | 114.2285 |
| n-Nonane | 128.2551 |
| n-Decane | 142.2817 |
| Nitrogen | 28.0134 |
| Oxygen | 31.9988 |
| Carbon Dioxide | 44.0095 |
| Carbon Monoxide | 28.0101 |
| Hydrogen Sulphide | 34.0809 |
| Water | 18.0153 |
| Hydrogen | 2.0159 |
| Helium | 4.0026 |
| Argon | 39.948 |
| 2,2-Dimethyl Propane | 72.1488 |
| 2-Methyl Pentane | 86.1764 |
| 3-Methyl Pentane | 86.1764 |
| 2,2-Dimethyl Butane | 86.1764 |
| 2,3-Dimethyl Butane | 86.1764 |
| Ethylene | 28.0532 |
| Propylene | 42.0797 |
| Methyl Alcohol | 32.0119 |
| Air | 28.9625 |
Calculation
Compressibility factor
The compressibility factor is calculated by:
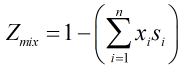
| Where | ||
|---|---|---|
| n | = | Number of constituents of natural gas mixture |
| xi | = | Mole fraction of ith component of natural gas mixture |
| si | = | Summation factor of ith component of natural gas mixture |
Ideal gross heating value (volumetric)
The volumetric ideal gross heating value is calculated by:
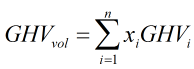
| Where | ||
|---|---|---|
| n | = | Number of constituents of natural gas mixture |
| xi | = | Mole fraction of ith component |
| GHVi | = | Ideal gross heating value of ith component |
Gross heating value (molar)
The molar gross heating value is calculated by:
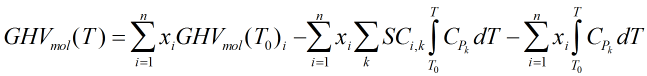
| Where | ||
|---|---|---|
| n | = | Number of constituents of natural gas mixture |
| T | = | Metering temperature |
| T0 | = | Reference temperature |
| xi | = | Mole fraction of ith component of natural gas mixture |
| GHVmol(T)i | = | Molar gross heating value of ith component of natural gas mixture |
| SCi,k | = | Stoichiometric coefficient of species k for combustion of ith component of natural gas mixture |
| Cp | = | Molar ideal heat capacity |
Wobbe Index
The Wobbe index is calculated by
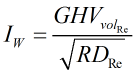
| Where | ||
|---|---|---|
| RDRe | = | Relative density of natural gas mixture |
| GHVVolRe | = | Real gas volumetric gross heating value of natural gas mixture |
