Wet Gas Orifice (Calc dens, Calc Std dens, Calc CV)
Options
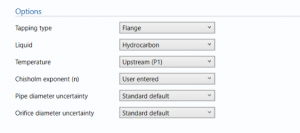
Tapping type
- Flange
- D/D2
- Corner
Select the tapping type in the orifice meter.
Note: Only required if ISO 5167 is selected.
Liquid
- Hydrocarbon
- Water
- Water-hydrocarbon mixture
Temperature
- Upstream (P1)
- downstream (P3)
Enter the temperature of the upstream or downstream flow.
Line density
- User entered
- Calculated
Enter whether the line density is user entered or calculated.
Chisholm exponent (n)
- User entered
- Calculated
This option is used to specify whether the n value used is calculated as per the standard or user entered.
Note: n has a (editable) default of 0.25 if user entered is selected as this is the value from Chisholm’s original correlation.
Pipe diameter uncertainty
- User entered
- Standard default
Enter whether the diameter of the pipe is user entered or the standard default.
Orifice diameter uncertainty
- User entered
- Standard default
Enter whether the diameter of the pipe is user entered or the standard default.
Pipe data
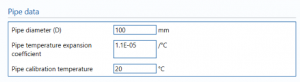
Pipe diameter (D) – Enter the diameter of the pipe.
Pipe temperature expansion coefficient – Enter the temperature expansion coefficient.
Note: the coefficient of expansion represents the change in size with respect to temperature.
Pipe calibration temperature – Enter the temperature at which the pipe was calibrated.
Process data
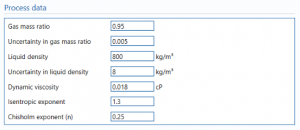
Gas mass ratio – the ratio of gas to total mass.
Uncertainty in gas mass ratio – Uncertainty in the ratio of gas to mass calculation or reading.
Line density – the density of the flow in the stream.
Uncertainty in Line density – Uncertainty in the density of the flow in the stream.
Hydrocarbon liquid density – the liquid hydrocarbon density of the flow in the stream.
Uncertainty hydrocarbon liquid density -Uncertainty in the liquid hydrocarbon density of the flow in the stream.
Water density – The density of water. Usually 1020 kg / m³
Uncertainty in water density – the uncertainty in the density of water.
Water liquid mass ratio – the ratio of water to liquid mass. Uncertainty in Water liquid mass ratio – the uncertainty of ratio of water mass to liquid mass.
Dynamic viscosity – the dynamic viscosity of the flow in the stream.
Note: Dynamic viscosity is the measure of the resistance to internal force of the fluid.
isentropic exponent – the isentropic exponent of gas.
Note: isentropic exponent is the ratio of the specific heat at constant pressure to specific heat at constant volume.
Chisholm exponent – The exponent used in Chisholm equation.
Note: n has a (editable) default of 0.25 if user entered is selected as this is the value from Chisholm’s original correlation.
Orifice data
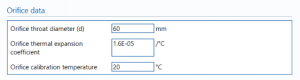
Orifice throat diameter – the diameter of the throat of the orifice.
Orifice thermal expansion coefficient – orifice thermal expansion coefficient.
Note: thermal expansion coefficient is the change in size per unit change in temperature.
Orifice calibration temperature – the calibration temperature of the orifice.
Uncertainty parameters
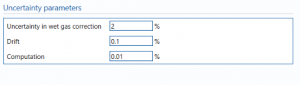
Uncertainty in wet gas – the uncertainty in wet gas percentage in the stream.
Drift – Additional uncertainty allowance due to meter drift from factors such as time, ambient temperature and line voltage. Normally left at zero, unless evidence is present to suggest a higher value.
Note: Drift is rarely apparent but needs to be continuously monitored through inspection, prevention and maintenance.
Computation – Uncertainty due to computational errors in flow computer.
Additional discharge coefficient uncertainty
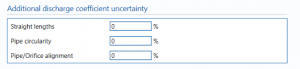
straight lengths – enter the percentage uncertainty due to straight lengths in pipe.
Pipe circularity – enter the percentage uncertainty due to circularity of the pipe.
Pipe/orifice alignment – enter the percentage uncertainty due to the alignment of the pipe and the orifice.
Intermediates
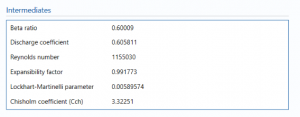
- Beta ratio
- Discharge coefficient
- Reynolds number
- Expansibility factor
- Lockhart-Martinelli parameter
- Chisholm coefficient
These parameters are calculated as per the inputs entered above.
Calculations
The uncertainty for the uncorrected gas mass flow rate, the corrected gas mass flow rate, gas standard volume flow rate and energy flow rate are calculated.
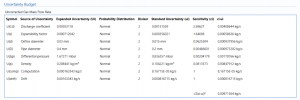
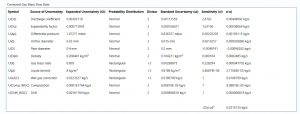
Uncertainty Budget
The uncertainty calculation is detailed in the uncertainty budget tables for the uncorrected gas mass flow rate, the corrected gas mass flow rate, gas standard volume flow rate and energy flow rate giving a break down of how the overall uncertainty is calculated for that parameter.
![]()
Uncertainties associated with these values are taken in as the Expanded Uncertainties. The Standard Uncertainty is calculated from dividing the Expanded Uncertainty by the coverage factor which is determined by the probability distribution that best suits that uncertainty component.
The Standard Uncertainty is then multiplied by the sensitivity value then squared. This is done for each parameter that contributes to the overall uncertainty in that parameter. The Standard Uncertainty in the parameter is the square root of the sum of each component variance as shown in the following equation:
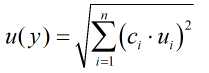
Calculated Uncertainty
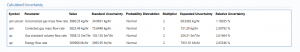
The Expanded Uncertainty is the Standard Uncertainty multiplied by the coverage factor (k). The coverage factor is defaulted to k = 2 (equivalent to a confidence level of approximately 95%). The Relative Uncertainty is the Expanded Uncertainty divided by the uncorrected gas mass flow rate, the corrected gas mass flow rate, gas standard volume flow rate or energy flow rate depending on the parameter.
