C108 – Meter K-factor Computation
Description
This calculates the meter k-factor for a meter proved using either a pipe prover, compact prover or a master meter.
References
Institute of Petroleum – Petroleum Measurement Manual: Part X – Meter Proving
Kelton calculation reference C108
FLOCALC calculation reference F066
KIMS calculation reference K119
Kelton calculation C219 – Table 54 Calculation of Ctl
Kelton calculation C220 – API Calculation of Compressibility Factor and Cpl
Kelton calculation C222 – API Calculation of Ctl (Product Groups)
Kelton calculation C223 IP Paper 2 – Compressibility & Cpl
Kelton calculation C251 – API Density Referral 2004
Kelton calculation C254 – API MPMS/GPA TP-27:2007 Ctl Calculation
Options
Calculate
- Meter K-factor
- Meter Factor
This option gives the choice to calculate K-factor and/or meter factor as the output.
Prover Type
- Pipe prover
- Master meter
- Compact prover
This option allow the user to choose what type of prover is being used.
Meter Type
- Mass
- Volume
This option is used to set whether the k-factor will be calculated in pulses/volume or pulses/mass.
Master Meter K-factor
- Fixed
- Varies with Reynold’s number
- Varies with flow rate
This option is used to determine what the master meter k-factor will be calculated against.
Ctlp
- None
- User entered
- Calculated
This option gives the user the option of applying a correction due to the temperature of the liquid at the prover.
Cplp
- None
- User entered
- Calculated
This option gives the user the option of applying a correction due to the pressure of the liquid at the prover.
Ctlm
- None
- User entered
- Calculated
This option gives the user the option of applying a correction due to the temperature of the liquid at the meter.
Cplm
- None
- User entered
- Calculated
This option gives the user the option of applying a correction due to the pressure of the liquid at the meter.
Ctsp
- None
- User entered
- Calculated – linear expansion coefficient
- Calculated – cubic expansion coefficient
This option gives the user the option of applying a correction due to the temperature on the steel of the prover.
Cpsp
- None
- User entered
- Calculated
This option gives the user the option of applying a correction due to the pressure on the steel of the prover.
Cpsp Calculation Method
- IP Manual Part X (D/Et)
- User entered coefficient
- Alternative calculation (2r/Et)
This option is used to select how to carry out the Cpsp calculation. It will be done according to IP Manual Part X. The pressure coefficient can be calculated as shown in the option either using pipe diameter, radius or a user enter coefficient.
Ctl Calculation Method
- ASTM-IP Table 54
- API Ch11.1 (1980)
- API Ch11.1 (2004)
- GPA TP-27 (2007)
If a temperature correction is required this option group will allow the user to select from one of these standards to implement a Ctl calculation .
Cpl Calculation Method
- IP Paper 2 (1984)
- API Ch11.2.1 (1984)
- API Ch11.2.2 (1986)
- API Ch11.1 (2004)
If a pressure correction is required this option group will allow the user to select from one of these standards to implement Cpl calculation.
Calculation
Correction for temperature on steel of prover
The Ctsp is calculated by:
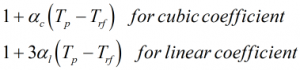
For a compact prover an additional correction is made on top of the calculation above to gain the Ctsp
![]()
| Where | ||
|---|---|---|
| αc | = | Cubic temperature coefficient |
| αl | = | Linear temperature coefficient |
| αd | = | Detector temperature coefficient |
| Tp | = | Prover temperature |
| Td | = | Compact prover detector temperature |
| Trf | = | Prover reference temperature |
Correction for pressure on steel of meter
The Cpsp is calculated by:
![]()
| Where | ||
|---|---|---|
| λ | = | Pressure coefficient |
| Pp | = | Prover pressure |
| Prf | = | Prover reference pressure |
Master meter K-factor
The master meter K-factor can be calculated against flow rate or Reynold’s number. This uses known test data and sets K-factor values against their corresponding Reynold’s number or flow rate. The flow rate/Reynold’s number is estimated from line conditions and prover geometry, linear interpolation is then employed to find the value of the K-factor. This process is done iteratively until a solution for K-factor has converged to necessary precision.
Uncorrected K-factor
The uncorrected K-factor is calculated by:
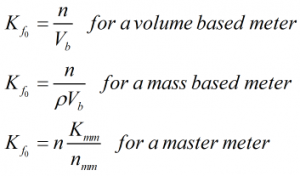
| Where | ||
|---|---|---|
| n | = | Number of pulses generated by the meter during a proving run |
| Vb | = | Base volume of prover |
| ρ | = | Observed density of liquid |
| nmm | = | Number of pulses generated by the master meter during proving run |
| Kmm | = | Master meter K-factor |
K-factor
The K-factor is calculated by:
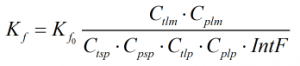
| Where | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kf0 | = | Uncorrected K-factor |
| Ctlm | = | Correction for temperature of the liquid at the meter |
| Cplm | = | Correction for pressure of the liquid at the meter |
| Ctlp | = | Correction for temperature of the liquid at the prover |
| Cplp | = | Correction for pressure of the liquid at the prover |
| Ctsp | = | Correction for temperature on steel of the prover |
| Cpsp | = | Correction for pressure on steel of the prover |
| IntF | = | Interpolation factor |
Meter Factor
The meter factor is calculated by:
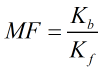
| Where | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kb | = | Base K-factor |
| Kf | = | K-factor |
